|
Learning Objectives:
-
Define and explain the
depreciation fund method or sinking fund method
of depreciation.
-
Prepare journal entries to record
depreciation under this method.
Contents:
Under depreciation fund method or sinking fund method, a fund is created
with the amount of annual depreciation. An amount
equal to annual depreciation is invested each year
in government papers or in some other gilt-edged
securities outside the business. The income earned
from investment is deposited into the fund and
immediately reinvested. This process is carried out
throughout the life of the asset and at the end of
its life a sum equal to the cost of the asset is
accumulated in the fund. Then the whole investment
is sold and a new asset is acquired with the sale
proceeds.
The special feature of this method is that the sum
required to buy the new asset is available from
depreciation or sinking fund. As a result, the
working capital of business is preserved. Sinking
fund method is specially applicable to costly
machines in large scale industries.
The entries to be made will be as follows:
At the end of the first year:
-
Debit profit and loss account
and credit depreciation fund account with amount
of annual depreciation.
-
Debit depreciation fund
investment account and credit bank account with
an equal amount.
At the end of each subsequent year:
-
Debit bank account and credit
depreciation fund account with amount of
interest earned on investment.
-
Debit profit and loss account
and credit depreciation fund account with amount
of annual depreciation.
-
Debit depreciation fund
investment account and credit bank account with
amount of annual depreciation plus interest
received.
In the last year:
-
Debit bank account and credit
depreciation fund account with amount of
interest earned on investment.
-
Debit profit and loss account
and credit depreciation fund account with amount
of annual installment.
-
Debit bank account and credit
depreciation fund investment account with
proceeds of sale of investment. Any profit or
loss on sale of investment should be transferred
to depreciation fund account.
-
Debit the account of new asset
and credit the bank account with cost of
replacement.
-
Debit depreciation fund account
and credit the account of old asset which has
now become useless.
Note: In the last year this
amount should not be invested in the purchase of
investments.
In the balance sheet that is
prepared during the period of building up the
depreciation fund, depreciation fund account shall
be shown on the liabilities side and depreciation
and depreciation fund investment account on the
asset side, whereas the asset for which this
depreciation fund is being created will appear at
its original cost.
The amount of annual depreciation to
be provided for the depreciation will be ascertained
from sinking fund table, an extract from which is
given below:
Sinking Fund Table
Periodic deposit which will amount
$1
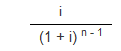
|
Period |
3% |
4% |
5% |
6% |
|
1 |
1.000000 |
1.000000 |
1.000000 |
1.000000 |
|
2 |
.492611 |
.490196 |
.487805 |
.485437 |
|
3 |
.323530 |
.320348 |
.317209 |
.314110 |
|
4 |
.239027 |
.235490 |
.232012 |
.228591 |
|
5 |
.188355 |
.184627 |
.180975 |
.117396 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
.154597 |
.150762 |
.147017 |
.143363 |
|
7 |
.130506 |
.126610 |
.122820 |
.119135 |
|
8 |
.112456 |
.108528 |
.104772 |
.101036 |
|
9 |
.098434 |
.094493 |
.090690 |
.087022 |
|
10 |
.087231 |
.083291 |
.079505 |
.075868 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
.053767 |
.049941 |
.046342 |
.042963 |
|
20 |
.037216 |
.033582 |
.030243 |
.027185 |
|
25 |
.027428 |
.024012 |
.020952 |
.018277 |
|
30 |
.021019 |
.017830 |
.015051 |
.012649 |
|
35 |
.016539 |
.013577 |
.011072 |
.008974 |
|
40 |
.013262 |
.010523 |
.008278 |
.006442 |
|
45 |
.010785 |
.008262 |
.006262 |
.004701 |
|
50 |
.008866 |
.006550 |
.004777 |
.003444 |
|
C acquires a 5 years' lease for
$40,000. It is decided to provide for the
renewal of lease immediately after 5 years by
setting up a depreciation fund. It is expected
that investment will fetch interest at 5% p.a.
Sinking fund table shows that $0.180975 invested
each year will produce $1 at the end of 5 years
at 5% p.a.
At the expiry of the lease, the
depreciation fund investments are sold for
$31,205 and immediately thereafter the lease is
renewed for a further period of 5 years by a
payment of $44,000.
Required: Make journal
entries.
Solution:
|
Annual depreciation =
40,000 ×
.180975 |
|
Journal Entries |
|
1st Year |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan. 1 |
Lease
Account |
Dr. |
40,000 |
|
| |
Bank Account |
|
|
40,000 |
| |
(Being lease
purchased for 5 years) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Profit and
loss Account |
Dr. |
7,239 |
|
| |
Depreciation fund Account |
|
|
7,239 |
| |
(Being
annual depreciation charged) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Depreciation
fund investment Account |
Dr. |
7,239 |
|
| |
Bank Account |
|
|
7,239 |
| |
(Being
amount of depreciation fund
invested) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
2nd Year |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Bank Account |
Dr. |
362 |
|
| |
Depreciation fund Account |
|
|
362 |
| |
(Being
interest received on
depreciation fund
investments) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Profit and
loss Account |
Dr. |
7,239 |
|
| |
Depreciation fund Account |
|
|
7,239 |
| |
(Being
annual depreciation charged) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Depreciation
fund investment Account |
Dr. |
7,601 |
|
| |
Bank Account |
|
|
7,601 |
| |
(Being
investment purchased) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
3rd Year |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Bank Account |
Dr. |
742 |
|
| |
Depreciation fund Account |
|
|
742 |
| |
(Being
interest received on
depreciation fund
investments) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Profit and
loss Account |
Dr. |
7,239 |
|
| |
Depreciation fund Account |
|
|
7,239 |
| |
(Being
annual depreciation charged) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Depreciation
fund investment Account |
Dr. |
7,981 |
|
| |
Bank Account |
|
|
7,981 |
| |
(Being
investment purchased) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
4th Year |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Bank Account |
Dr. |
1,141 |
|
| |
Depreciation fund Account |
|
|
1,141 |
| |
(Being
interest received on
depreciation fund
investments) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Profit and
loss Account |
Dr. |
7,239 |
|
| |
Depreciation fund Account |
|
|
7,239 |
| |
(Being
annual depreciation charged) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Depreciation
fund investment Account |
Dr. |
8,380 |
|
| |
Bank Account |
|
|
8,380 |
| |
(Being
investment purchased) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
5th Year |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Bank Account |
Dr. |
1,560 |
|
| |
Depreciation fund Account |
|
|
1,560 |
| |
(Being
interest received on
depreciation fund
investments) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Profit and
loss Account |
Dr. |
7,239 |
|
| |
Depreciation fund Account |
|
|
7,239 |
| |
(Being
annual depreciation charged) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Bank Account |
Dr. |
31,205 |
|
| |
Depreciation fund investment
Account |
|
|
31,205 |
| |
(Being
depreciation fund
investments sold) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Depreciation
fund investment Account |
Dr. |
4 |
|
| |
Depreciation fund Account |
|
|
4 |
| |
(Being the
profit on the sale of
investment transferred to
depreciation fund account) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Depreciation
fund Account |
Dr. |
40,004 |
|
| |
Lease Account |
|
|
40,004 |
| |
Profit and loss Account |
|
|
|
| |
(Depreciation fund account
transferred to lease
account) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Lease
Account |
Dr. |
44,000 |
|
| |
Bank Account |
|
|
44,000 |
| |
(Being new
lease purchased for 5 years) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
There is very close relationship
between annuity method and depreciation fund
method. Under both the method:
-
Compound interest is taken
into account.
-
Provision is made for the
replacement of asset.
-
There are equal annual
charges to revenue.
Depreciation fund method assumes
a constant rate of return on investments in
identical securities. This is hardly true,
because rates of interest do vary every now and
then. Variation of rate upsets the earlier
periodic allocation of depreciation and entails
recitation. Further the amount realized on sale
of security rarely agrees with its acquisition
cost due to market fluctuations. This method
cannot be used where any additions are made to
an asset during the year.
|