Delivery Cycle Time
A Measure of Internal
Business Process Performance:
Delivery cycle time is an important measure
of internal business process performance.
Performance measures are found on the
balanced scorecards of the companies. Examples of the some
performance measures can be found on
characteristics of balanced scorecard page. Most
of the performance measures are self explanatory.
However, three are not - delivery cycle time,
throughput time, and manufacturing cycle efficiency
(MCE). On this page, deliver cycle time is defined,
explained and calculated.
Definition and Explanation:
The
amount of time from when an order is received from a
customer to when the completed order is shipped is
called delivery cycle time. This time is
clearly a key concern to many customers, who would
like the delivery cycle time to be as short as
possible. Cutting the delivery cycle time may give a
company a key competitive advantage - and may be
necessary for survival. Consequently, many companies
would include this performance measure on their
balanced scorecard.
Delivery Cycle Time and Throughput (Manufacturing
Cycle) Time
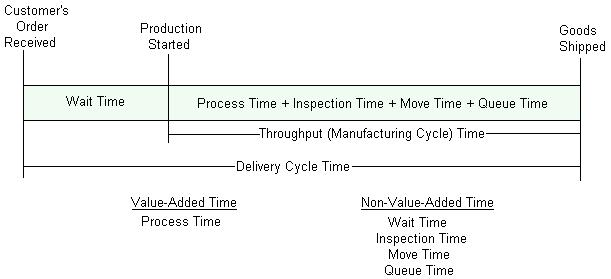
Formula:
|
Delivery Cycle Time = Wait time +
Throughput time |
Example
Calculation of
Delivery Cycle Time:
Novex Company keeps
careful track of the time relating to orders and
their production. During the most recent quarter,
the following average times were recorded for each
unit or order:
| Wait
time |
17.0 |
|
Inspection time |
0.4 |
|
Process time |
2.0 |
| Move
time |
0.6 |
| Queue
time |
5.0 |
Goods are shipped as soon as production is
completed.
Required:
Calculate the
delivery cycle time.
Solution:
Delivery Cycle Efficiency = Wait time + Through
=
17.0 days + 8.0 days*
=
25.0 days
*Throughput
time = Process time + Inspection time + move time +
Queue time
2.0
days + 0.4 days + 0.6 days + 5.0 days
= 8.0
days
Relevant Articles:
|