|
When
the acceptor of a bill of exchange is a reputable
person the bill is as good as money, and any bank
will discount it.
Definition and Explanation of
Discounting a Bill:
If the
drawer of the bill does not want to wait till the
due date of the bill and is in need of money, he may
sell his bill to a bank at a certain rate of
discount. The bill will be endorsed by the drawer
with a signed and dated order to pay the bank. The
bank will become the holder and the owner of the
bill. After getting the bill, the bank will pay cash
to the drawer equal to the face value less interest
or discount at an agreed rate for the number of days
it has to run. This process is know as
discounting of a bill of exchange.
Example:
For
example, a drawer has a bill for $10,000. He
discounted this bill with his bank two months before
its due date at 15% p.a. rate of discount. Discount
will be calculated as the follow:
1,000 × 15/100 × 2/12 = 250
Thus
the drawer will receive a cash worth $9,750 and will
bear a loss of $250.
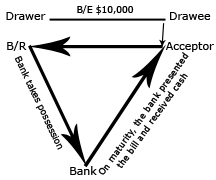
The bank will keep
this bill in possession till the due date. On
maturity (due date) the bank will present the bill
to the acceptor and will receive cash from him (if
the bill is honored). In case, the acceptor does not
make the payment to the bank, then the drawer on any
person who has discounted the bill have to take this
liability and will pay cash to the bank.
Until the bill is
honored on the due date, there is always a chance
that the drawer will become liable on the bill. This
is called a contingent liability - a liability that
will only arise if a certain event occurs - the
acceptor does not honor the bill.
 |
|
Drawer
discounted the bill for $9,750 and suffered a
loss of $250. In other words drawer had to
pay the price in order to receive the cash
before maturity. |
When a bill is
discounted by the holder, the following entries are
passed in the books of drawer, drawee and bank:
When the bill is
drawn by the drawer (A) and accepted by drawee (B)
|
Drawer's
Journal |
Drawee's
Journal |
B/R
A/C..................XXX
B A/C..................XXX
(Acceptance received) |
A
A/C..................XXX
B/P A/C.................XXX
(Acceptance given) |
|
When a bill is
discounted at bank: Bank A/C......................XXX
Discount A/C.................XXX
B/R A/C....................XXX
(Bill discounted at bank) |
No journal entry at the time of discounting
of bill in the books of drawee.
|
The entry for
discounting a bill in drawer's journal shows
increase in drawer's bank balance at present value
(face value - discount given), increase in a loss
(discount given) and decrease in an asset (bill
receivable).
The entry in the
journal of bank will be as under:
When a bill is
discounted at bank:
B/R A/C............XXX
Drawer A/C........XXX
Discount A/C.....XXX
(Bill discounted)
This journal entry
indicates, increase in assets (B/R) in the bank,
increase in a liabilities (the amount transferred to
the drawer's account) and in revenue for the bank
(discount).
When the bank
presented the bill to the acceptor on maturity date
and the acceptor met his obligation, the following
entries are passed:
|
Drawer's
Journal |
Drawee's
Journal |
Bank's Journal |
|
No entry in
the books of drawer. |
Bill payable
A/C...XXX
Cash A/C.........XXX
(Acceptance honored and cash paid to bank on
presentation of the bill) |
Cash
A/C.......XXX
B/R A/C.........XXX
(Cash received from acceptor equal to full
value of the bill) |
Note that the drawee pays full amount of the
bill to the bank at the time of maturity but
bank pays face value less discount to the drawer
when drawer discounts the bill with the bank.
This difference (discount) is revenue of the
bank and expense of the drawer. |